
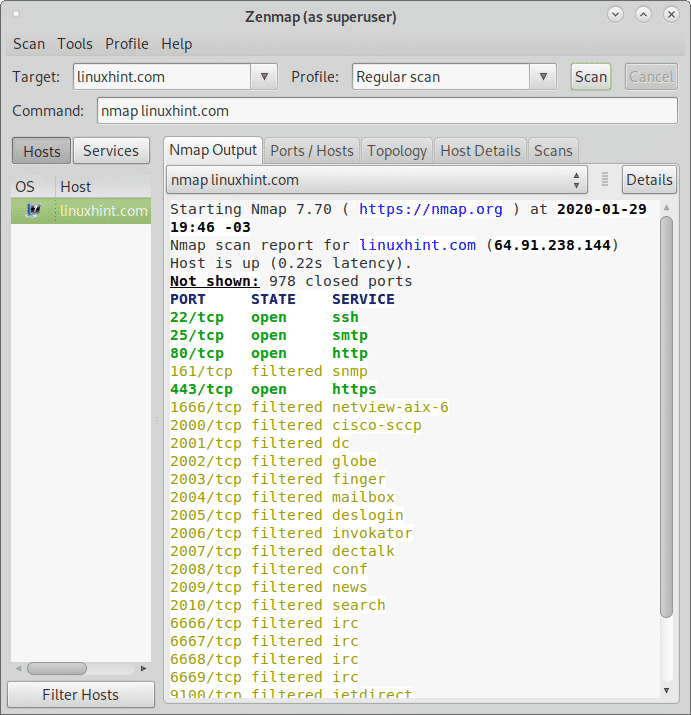
Performing your first scan with nmap # nmap -sn In addition, Nmap sends an ARP request for any hosts on the local network, filling in MAC address details. That’s why, by default, Nmap performs host discovery by sending four different probes: An ICMP type 8 (echo request), an ICMP type 13 (timestamp request), a TCP SYN packet to port 443, and a TCP ACK packet to port 80. While this might sound like a simple task, consider that a Class A network (10.0.0.0/8) has over 16 million available addresses. Making the job more difficult, most modern firewalls block ICMP echo (ping) requests. The first step in learning about a new network is to determine what's attached to your network and which services are exposed.
#Zenmap subnet scan how to#
Here's how to discover what's on your network. More than just a fancy ping sweep, with the right scans, Nmap can fill in your new network diagram with the MAC address, open ports, operating system (OS), and services of the hosts on your network. There’s no better tool to solve the problem of an unfamiliar and undocumented network than Nmap. Warning: Your employer might interpret network scanning as an attack. Please be sure you’re authorized to use Nmap before performing any scans. If you’re new to Nmap and you need to get to know your network, then read on. This is not an article about security auditing, penetration testing, or other advanced Nmap use cases. As such, it covers simple Nmap flags to help somebody inside the network discover hosts and facts about them. This article is for discovering the scope of a network as a sysadmin in a new environment. Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS security FAQ.Here you can see a device with hostname MSRTK has IP address 192.168.1.8. Nmap done: 256 IP addresses (4 hosts up) scanned in 2.41 seconds Nmap scan report for ubuntu (192.168.1.5) Nmap scan report for hpprinter (192.168.1.2) For each device that responds to the ping, the output shows the hostname and IP address like so: Starting Nmap 6.40 ( ) at 12:46 GMT Ping scan just pings all the IP addresses to see if they respond. Now use the nmap command with the -sn flag (ping scan) on the whole subnet range. Now you have the IP address of your computer, you will scan the whole subnet for other devices.
On Windows, go to the Control Panel, then under Network and Sharing Center, click View network connections, select your active network connection and click View status of this connection to view the IP address.On macOS, go to System Preferences then Network and select your active network connection to view the IP address.On Linux, type hostname -I into a terminal window.First find your own IP address, in other words the one of the computer you’re using to find your MSRTK Moduls IP-address: To use nmap to scan the devices on your network, you need to know the subnet you are connected to.
#Zenmap subnet scan install#
#Zenmap subnet scan free#
The nmap command (Network Mapper) is a free and open-source tool for network discovery, available for Linux, macOS, and Windows.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
